The electric charge is present all
around us. Still, man remained unwire of the electric power forges. He tried it
explain the lightning in the sky through various imaginary interpretations
which were not satisfactory. Then the Greek philosopher. Thales lifted the
curtain from this mystery. He discovered, around 600 BC. That the same effect
which was visible during lightning in the sky also appeared in a piece of amber
when it was rubbed against fur. The friction against fur produced in amber the
property of attracting light substance like straw, feather and paper. The Greek
word for amber is ‘electron’. So Thales called this mysterious power
“electric”.
About 2,000 years after Thales discovery, William Gilbert, an
English scientist, made another discovery. Experimenting with amber and loadstone, he discovered the basic
difference between electric and the magnetic attraction. William used the terms
‘electrical;. For the things like glass and sculpture which behaved like amber.
And he used the word electricity to describe the natural phenomena associated
with these things.
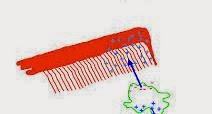
Here is an easy
experiment to make you understand the phenomenon of lightning. Brush your hair
with a comb in a dark room. Then, bring the comb close to your thumb. You will
now, brush your dry hair with a plastic comb and try to listen. When did you
hear? A cracking sound! Bring the comb close to small bits of paper. These are
attracted towards the comb! The reason: when you brush your dry hair with the comb.
It gets charged and can attract small bits of paper.
A glass rod and an ebonite rod can
also attract small bit of paper when they are rubbed against a piece of skill
and cat’s hide, respectively. When an object receive the property of attracting
other object. It is called charging. This may happen when the object is rubbed
against another object or comes, close to it, or simply gets in contact with
it. The charge in the glass rod. The glass rod has charge in the ebonite rod.
The glass rod has the positive charge and the charge in the ebonite rod is
called the negative together. When two similar charges are brought together,
they attract each other, neutral rod gets charged when brought close to a
charged rod. With the removal of the charged rod. The other rod again becomes
neutral. This effect is called the Electrostatic Induction. What is the nature
of the charge and the difference between the positive and the negative charges?
Man still does not know.




.jpg)


